Tibet Geography
Located on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of southwest China, the Tibet Autonomous Region has an area of 1,220,000 square meters, 12.8% of the total area of China. It borders the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region and east Qinghai in north side and borders Yunnan Province and southeast Sichuan in south side. Close to the south and west Tibet lie Burma, India, Bhutan, Sikkim and Nepal.
Tibet Autonomous Region has very complex topography with an average elevation of more than 4000 meters. It can be divided into three geography parts: the North-Tibet Plateau in the west, the south Tibet Valley and the Henduan Ranges in the east.
The North-Tibet Plateau takes up 2/3 of the total area of Tibet including the area among the Kunlun Mountain, Kangdese Mountain, Tonglha Mountain and Nyainqentanglha Mountain. The south part is mainly consisting of valleys between Kangdese Mountains and Himalayas where the Yarlung Zangbo River passes. The east part of which is made up of high mountains and big valleys lying from north to south is the main section of Henduan Ranges.
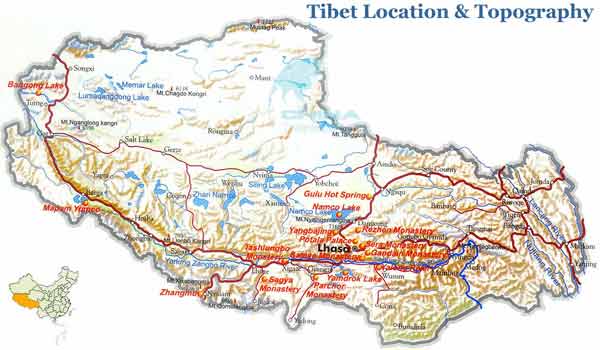 Tibet can be divided into three geography parts: the North-Tibet Plateau in the west, the south Tibet Valley and the Henduan Ranges in the east.
Tibet can be divided into three geography parts: the North-Tibet Plateau in the west, the south Tibet Valley and the Henduan Ranges in the east. BACK
BACK
0 Comment ON "Tibet Geography"